事件监听
将支线业务(独立小功能)在监听器中实现,而不是在主线业务逻辑中实现。既能实现功能的复用,又便于对功能的修改(组件化、功能可增加或删除)。
事件类型
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
public class MyApplicationEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public MyApplicationEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}
事件监听器
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyEmailListener implements ApplicationListener<MyApplicationEvent> {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyEmailListener.class);
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyApplicationEvent event) {
String source = (String) event.getSource();
LOGGER.error("接收来自" + source + "的消息");
LOGGER.error("EmailListener向用户发送邮件");
}
}import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MySMSListener implements ApplicationListener<MyApplicationEvent> {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MySMSListener.class);
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyApplicationEvent event) {
String source = (String) event.getSource();
LOGGER.error("接收来自" + source + "的消息");
LOGGER.error("SMSListener向用户发送短信");
}
}从函数式接口演化成注解的有很多,例如 Controller 和 @Controller、Servlet 和 @WebServlet。
每一个注解标注的方法,本质上都对应了一个接口的匿名实现类,同时创建了该匿名类的对象放入到容器中。后面通过模拟实现 @EventListener 注解对这个问题做进一步的了解。
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyListeners {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyListeners.class);
@Order(5)
@EventListener
public void callQQPhone(MyApplicationEvent event){
LOGGER.error("正在拨打QQ电话");
}
@Order(6)
@EventListener
public void callWechatPhone(MyApplicationEvent event){
LOGGER.error("正在拨打微信电话");
}
@Order(3)
@EventListener
public void callVideoPhone(MyApplicationEvent event){
LOGGER.error("正在拨打视频电话");
}
@Order(2)
@EventListener
public void callAudioPhone(MyApplicationEvent event){
LOGGER.error("正在拨打音频电话");
}
}事件发布器
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class MyApplicationService {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyApplicationService.class);
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
public void doWork() {
LOGGER.error("Service: 核心业务");
// TODO:
// 1. 事件的源应该放入什么东西还不确定
// 2. 如果需要doWork传入一些信息给监听器对象, 如何通过这个事件来传递呢?
// 3. 如何控制监听器的执行顺序, 例如, 先执行发送邮件, 后执行发送短信. 答: 通过额外的@Order注解
ApplicationEvent event = new MyApplicationEvent(MyApplicationService.class.getName());
publisher.publishEvent(event);
}
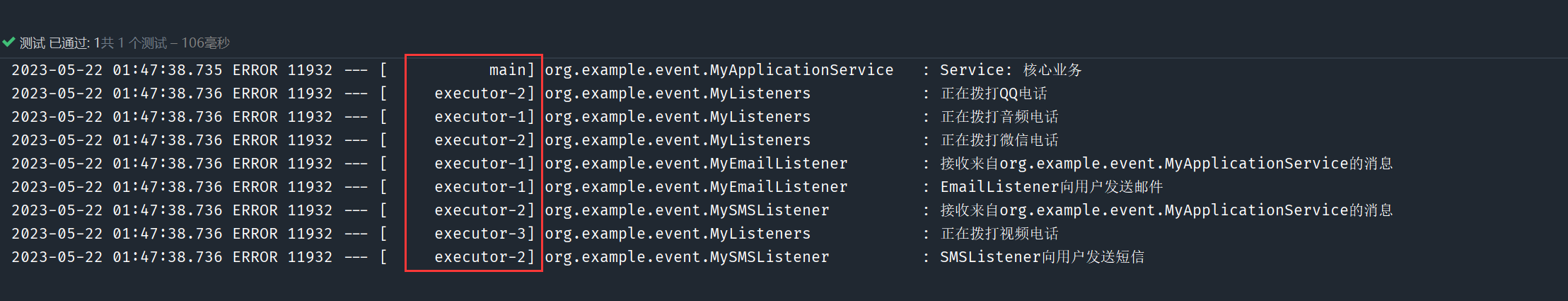
}优化
利用线程池来异步的发送事件,默认情况下是单线程发送。
默认使用的发送事件的广播器是
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,为其设置线程池对象即可实现异步发送。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Configuration
public class SimpleApplicationEventMulticasterConfig {
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(3);
taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(10);
taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(100);
return taskExecutor;
}
/**
* 这里的Bean的名字必须是applicationEventMulticaster, 如果名字不一样会导致无法覆盖.
* 这说明这个类的自动配置类写的不够好, 没有用@ConditionOnBean和@ConditionOnMissingBean配合使用解决这个问题
* 1. 在后面遇到类似的问题时, 如果需要找到该Bean对应的beanName, 可以通过 context.getBeanNamesForType() 来查看容器中的 bean
* 2. 可以通过getBean()获取该 bean 对象, 通过debug来查看其需要配置什么信息
*/
@Bean
public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster applicationEventMulticaster(ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor) {
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster multicaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
multicaster.setTaskExecutor(executor);
return multicaster;
}
}
模拟实现 @EventListener 注解
自定义注解 @MyEventListener
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyEventListener {
}使用 @MyListener 注解
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyListeners {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyListeners.class);
// 省略先前@EventListener注解标注的重复的代码
// ...
@MyEventListener
public void sendAd(MyApplicationEvent event){
LOGGER.error("正在使用自定义的@MyEventListener注解来打广告");
}
}解析 @MyEventListener 注解
import org.example.event.MyApplicationService;
import org.example.event.MyEventListener;
import org.example.event.MyListeners;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@SpringBootTest
public class MyEventListenerResolver {
@Autowired
ApplicationContext context;
@Test
public void myEventListenerTest() {
MyApplicationService service = context.getBean(MyApplicationService.class);
//TODO: 这里可以通过getBeanDefinitionNames来获取容器中所有的Bean对象, 对所有的Bean都进行下面的判断
MyListeners myListenersBean = context.getBean(MyListeners.class);
Method[] methods = myListenersBean.getClass().getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
// 如果方法中出现了自定义的@MyEventListener注解
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyEventListener.class)) {
// 每一个注解标注的方法都对应一个接口的匿名实现类
// 对于每一个标注了@MyEventListener注解的方法都会生成一个ApplicationListener匿名实现类的对象
// 这是适配器模式的一种体现, 将注解标注的方法转化成一个类对象
/* ApplicationListener applicationListener = new ApplicationListener() {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
// @MyEventListener注解标注的方法 <=> ApplicationListener接口中的方法
// 流程:
// => 找到注解标注的方法
// => 创建ApplicationListener接口的实现类: new ApplicationListener
// => 实现接口方法, 方法具体内容即为注解标注的方法, 因此存在反射调用: onApplicationEvent()
// => 将ApplicationListener注册到Spring容器中
try {
// TODO: 这里能够正常显式解析出@MyEventListener, 注册ApplicationListener到容器中也没问题,
// 执行也能够调用sendAd()方法, 但是会有一条argument type mismatch的错误. 如何处理这个问题呢?
// 答: 因为这里创建的ApplicationListener没有使用泛型, 所有所有类型的事件都会被该对象监听到. 但是实际反射调用的method方法却只能够处理MyEventListener类型的事件
// 这里是在单元测试的时候会自动关闭容器, context.close()也会发送一条事件, 此时类型不匹配从而产生该问题
// 处理方法:
// (1). 为new ApplicationListener添加泛型, 可以将解析器类设置为泛型类.
// (2). 在onApplicationEvent中处理, 即监听所有事件类型, 但是只处理一部分类型的事件, 该方式感觉更加通用一些
method.invoke(myListenersBean, event);
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};*/
ApplicationListener<MyApplicationEvent> applicationListener = new ApplicationListener<MyApplicationEvent>() {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyApplicationEvent event) {
try {
method.invoke(myListenersBean, event);
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
// 向容器中添加解析生成的ApplicationListener
if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext = (AbstractApplicationContext) context;
applicationContext.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);
}
}
}
// 测试service的功能
service.doWork();
}
}出现 argument type mismatch的错误. 如何处理这个问题呢?
答: 因为这里创建的ApplicationListener没有使用泛型,所有所有类型的事件都会被该ApplicationListener的匿名类对象监听到。但是实际反射调用的method方法却只能够处理MyEventListener类型的事件。而在进行单元测试的时候,会自动关闭容器,context.close()也会发送一条事件,此时类型不匹配从而产生该问题。
处理方法:
- 为new ApplicationListener添加泛型,进一步为了追求不写死还可以将解析器类设置为泛型类。
- 在onApplicationEvent中处理,即监听所有事件类型,但是只处理一部分类型的事件,该方式感觉更加通用一些。
小小的形式上优化
上面为了测试,在测试类中进行手工解析,进一步可以使用 SmartInitializingSingleton 对象,该对象可以在所有的单例Bean对象创建完成之后回调其中的方法。因此这里将解析@MyEventListener注解的方法写入到其中,小小地优化一下,在测试代码中只需要调用service中的doWork()方法即可。
/**
* 在所有的单例对象创建完成后, 会回调该对象中的方法
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public SmartInitializingSingleton smartInitializingSingleton(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
return new SmartInitializingSingleton() {
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
String[] names = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
Object bean = context.getBean(name);
Method[] methods = bean.getClass().getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(MyEventListener.class)) {
ApplicationListener applicationListener = new ApplicationListener() {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
System.out.println(event);
try {
Class<?> eventType = method.getParameterTypes()[0];
if (event.getClass().equals(eventType)) {
// eventType.isAssignableFrom(event.getClass()) 有什么不同?
method.invoke(bean, event);
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
// 向容器中添加解析生成的ApplicationListener
if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext = (AbstractApplicationContext) context;
applicationContext.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);
}
}
}
}
}
};
}事件发布
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.GenericWebApplicationContext;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
/**
* TODO: 目前存在bug
*/
@Component
public class MyApplicationEventMulticaster extends MyAbstractApplicationEventMulticaster {
private Set<ApplicationListener> applicationListeners = new HashSet<>();
@Autowired
private GenericWebApplicationContext context;
/**
* 用来收集监听器
*
* @param listenerBeanName
*/
@Override
public void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {
System.out.println("listenerBeanName = " + listenerBeanName);
ApplicationListener applicationListenerBean = (ApplicationListener) context.getBean(listenerBeanName);
System.out.println("applicationListenerBean = " + applicationListenerBean);
applicationListeners.add(applicationListenerBean);
}
/**
* 发布事件, 当调用publisher.publishEvent()方法时, 底层会调用该方法
*
* @param event
* @param eventType
*/
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
applicationListeners.forEach(
applicationListener -> {
// TODO: 这里如何仅仅通过JDK的反射来获取到类中接口的泛型类型
ResolvableType genericType = ResolvableType.forClass(applicationListener.getClass()).getInterfaces()[0].getGeneric();
if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(genericType)) {
// 使用线程池来优化事件发送
executor.submit(() -> {
applicationListener.onApplicationEvent(event);
});
}
});
}
}


