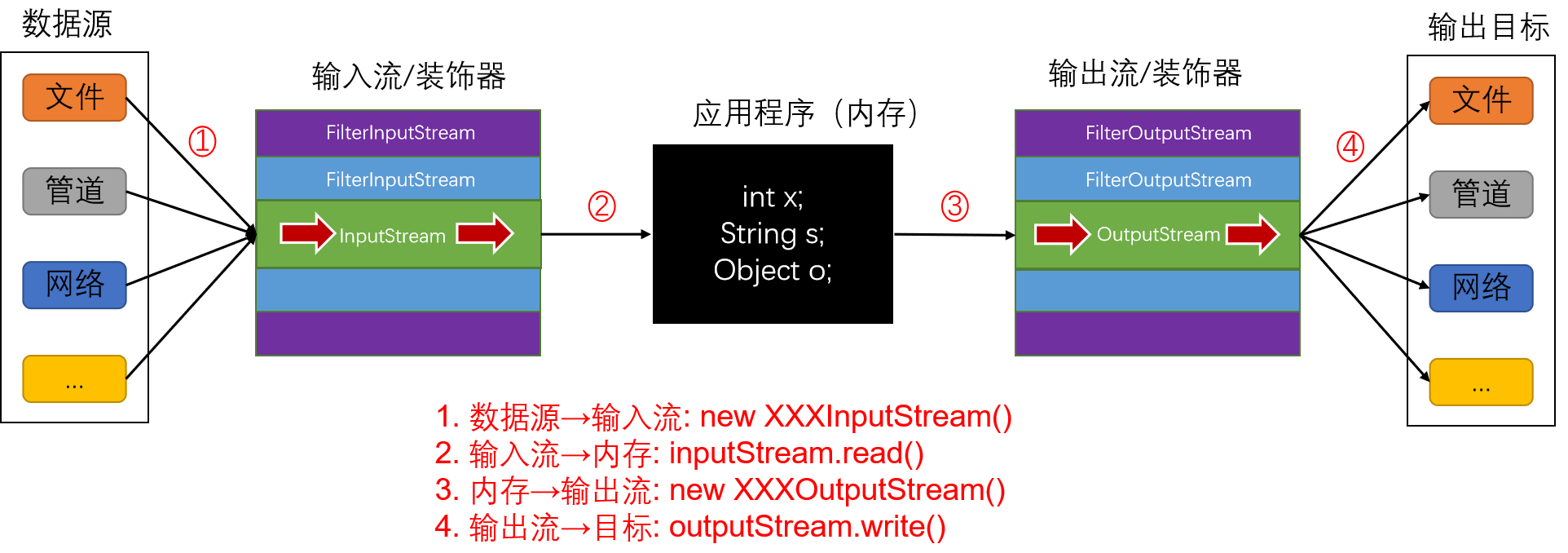
IO流
设计理念
通过装饰器模式,通过叠加多个对象来获得所期望的功能。
- 字节流(InputStream、OutputStream)对应原生的二进制数据
- 字符流(Reader、Writer)对应字符数据,会自动处理与本地字符集之间的转换
- 缓冲流(Buffer)可以提高性能,减少底层API的调用次数来优化I/O。设计者更优雅的实现是将缓冲流作为一种默认的行为,这样可以避免每次都要包装一层缓冲流,可惜并没有这么做。
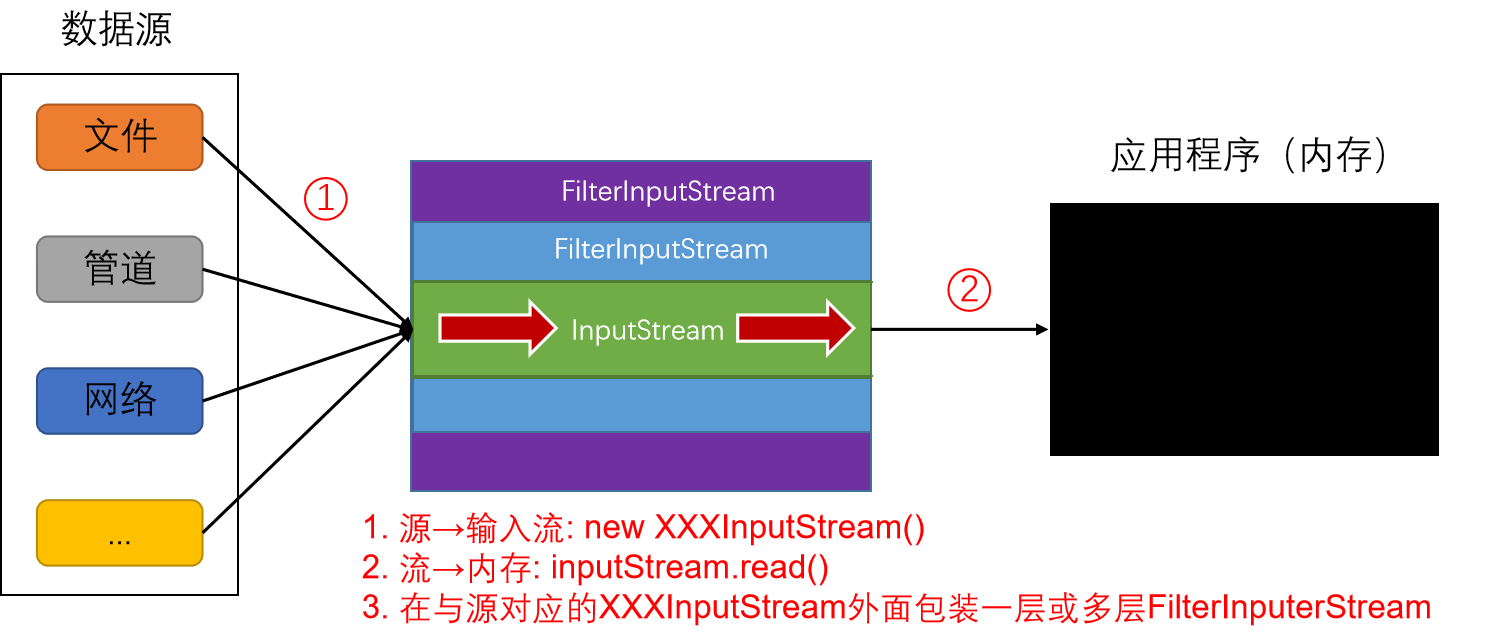
输入流类型
InputStream
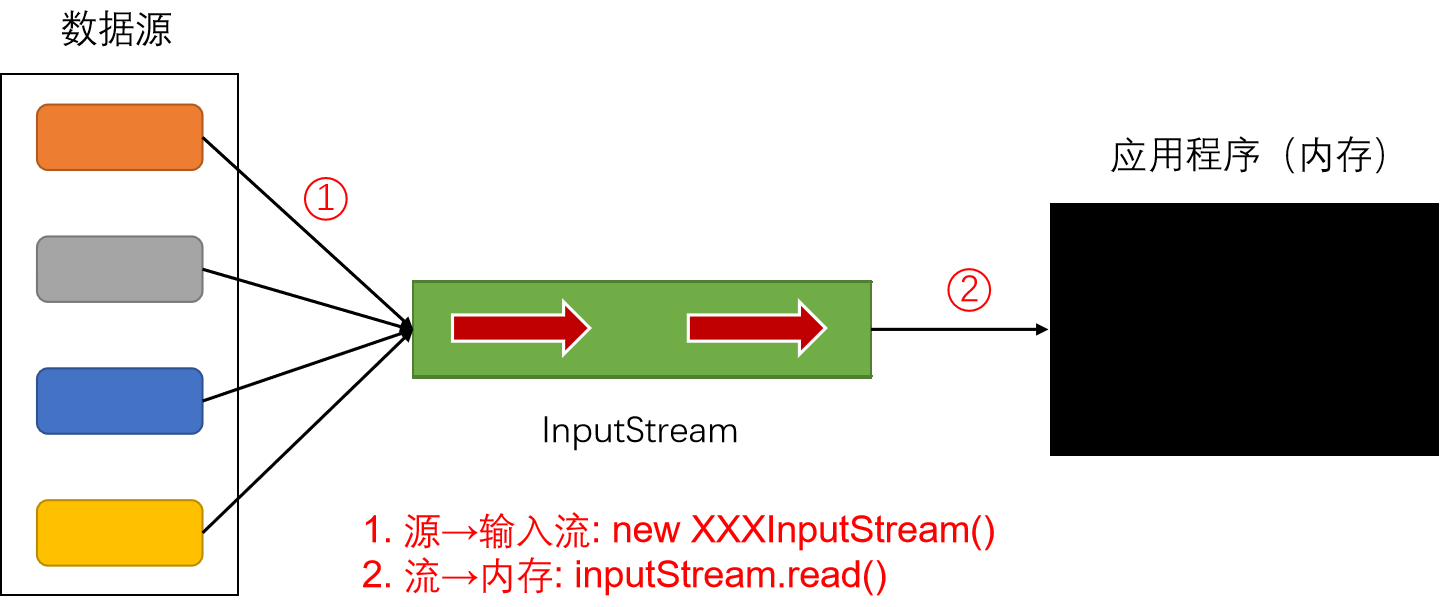
InputStream 表示从不同数据源产生输入的类,每种数据源都对应一种 InputStream 子类,数据源有:
- 字节数组
- String 对象(被废弃)
- 文件
- 管道(多线程)
- 一个其它种类的流组成的序列,可以把多个流汇聚成一个流
- Socket 连接
除了上面对应数据源的 InputStream 外,还有作为装饰器接口的 FilterInputStream 同样集成了 InputStream。
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class ReadTest {
private static String s;
// [72, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 87, 111, 114, 108, 100]
private static byte[] inputBytes;
private static byte[] outputBytes;
private static String inputFileName;
private static String inputFile2Name;
private static String outputFileName;
private String classpath;
private Path inputFilePath;
private Path inputfile2Path;
private Path outputFilePath;
static {
s = "Hello World";
inputBytes = s.getBytes(Charset.defaultCharset());
outputBytes = new byte[1024];
inputFileName = "input.txt";
inputFile2Name = "input2.txt";
outputFileName = "output.txt";
}
{
classpath = getClass().getResource("/").getPath().substring(1);
inputFilePath = Paths.get(classpath, inputFileName);
inputfile2Path = Paths.get(classpath, inputFile2Name);
outputFilePath = Paths.get(classpath, outputFileName);
}
/**
* 每个InputStream都会有read()方法
*/
@Test
public void readTest() throws IOException {
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(inputBytes);
for (int i = 0; i < inputBytes.length; i++) {
int read = byteArrayInputStream.read();
System.out.println(read);
}
byteArrayInputStream.close();
}
/**
* 使用read()方法的约定来退出循环, 可应用于长度不确定的字节流
*/
@Test
public void read2Test() throws IOException {
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(inputBytes);
int read;
while ((read = byteArrayInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(read);
}
byteArrayInputStream.close();
}
/**
* StringBufferInputStream被废弃, 对于字符串, 推荐使用StringReader来创建流
*/
@Test
public void read3Test() {
StringBufferInputStream stringBufferInputStream = new StringBufferInputStream(s);
}
@Test
public void read4Test() throws Exception {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(inputFilePath.toFile());
int read;
while ((read = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(read);
}
}
@Test
public void read5Test() throws Exception {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(inputFilePath.toFile());
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(outputFilePath.toFile());
int read;
while ((read = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(read);
fileOutputStream.write(read);
}
}
@Test
public void read6Test() {
PipedInputStream pipedInputStream = new PipedInputStream();
}
@Test
public void read7Test() throws Exception {
FileInputStream fileInputStream01 = new FileInputStream(inputFilePath.toFile());
FileInputStream fileInputStream02 = new FileInputStream(inputfile2Path.toFile());
SequenceInputStream sequenceInputStream = new SequenceInputStream(fileInputStream01, fileInputStream02);
int read;
while ((read = sequenceInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char) read);
}
}
}Reader
Reader 的出现不是用来替代 InputStream,InputStream 面向字节,而 Reader 面向字符,同时 Reader 提供兼容 Unicode 的功能。
为了将来自“字节”层次中的 InputStream 和来自“字符”层次中的 OutputStream 结合起来使用,需要使用到适配器类:InputStreamReader 可以将 InputStream 转换为 Reader。
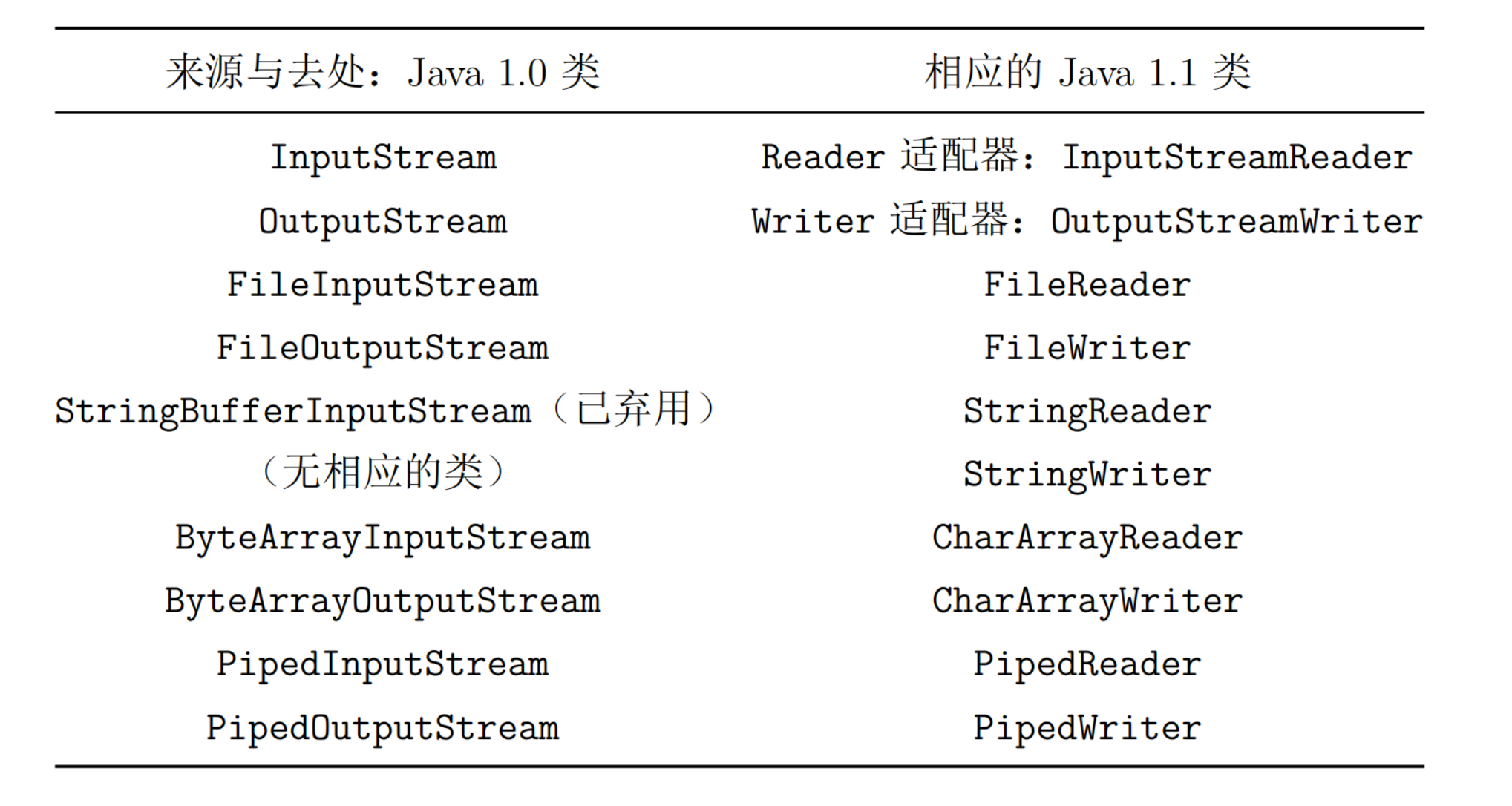
在 InputStream 的体系中,装饰器类都是 FilterInputStream 的子类。但是在 Writer 体系中,装饰器类并不是 FilterWriter 的子类
输出流类型
该类别决定了输出要去往的目标:字节数组、文件或管道。
- 字节数组:ByteArrayOutputStream
- 文件:FileOutputStream
- 管道:PipeOutputStream
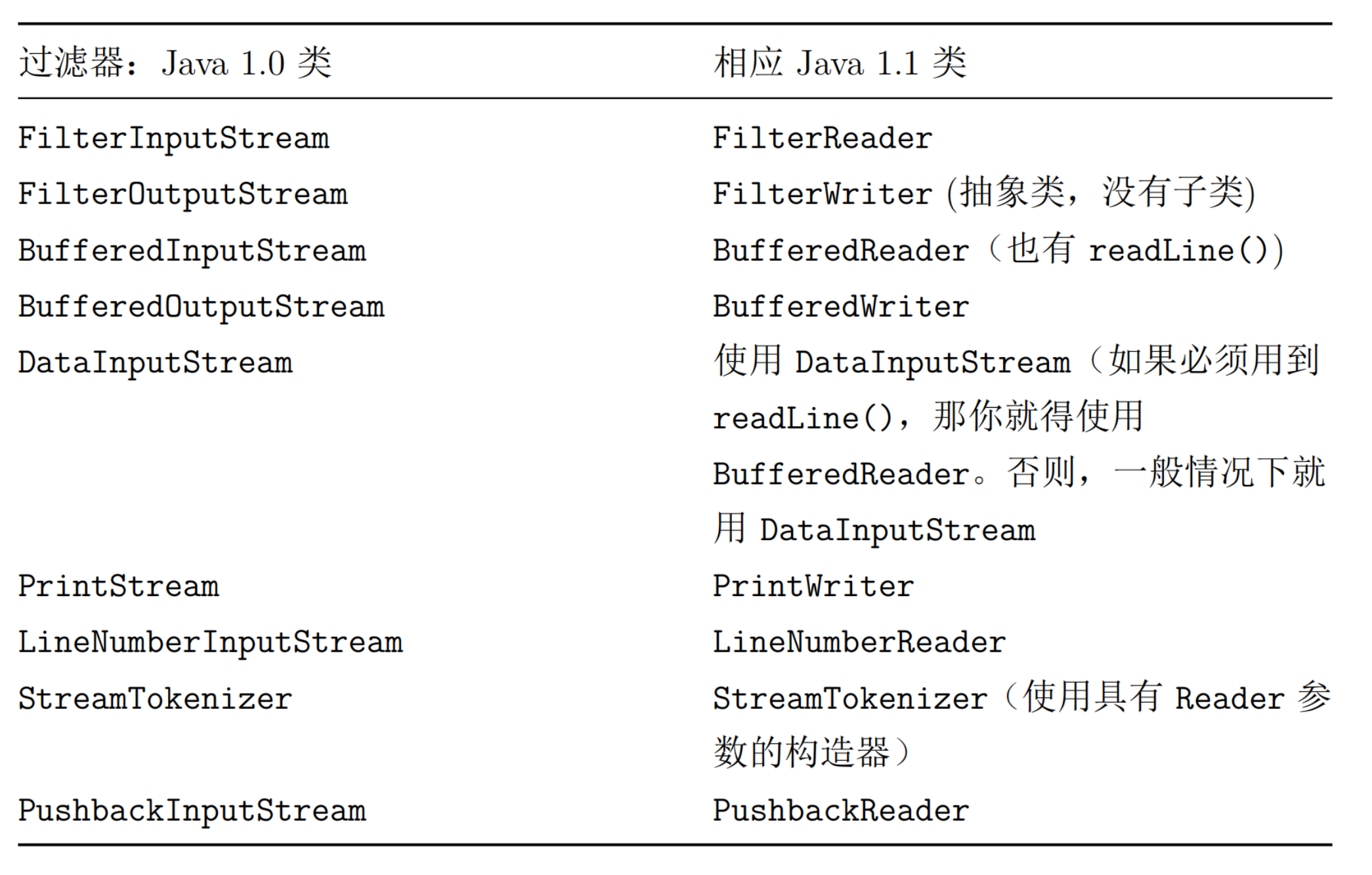
装饰器流 FilterInputStream/FilterOutputStream
装饰器模式
之所以存在 FileterInputStream 类,是因为让 FilterInputStream 作为所有装饰器类的基类。
装饰器必须具有和它所装饰对象相同的接口,但装饰器类也可以扩展一些接口
FilterInputStream
DataInputStream
DataInputStream 允许读取不同的基本数据类型和String类型的对象,例如readByte()、readFloat()等,将
BufferedInputStream
几乎所有的流行为都需要添加缓冲流来提高效率,没有作为默认行为是设计上的一个失败。
FilterOutputStream
DataOutputStream
BufferedOutputStream
可以调用 flush() 方法清空缓冲区
PrintStream
没有处理好国际化的问题,在PrintWriter中得到解决。
RandomAccessFile 类
附录:Maven项目路径和系统环境路径
获取Module模块的根路径
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import java.nio.file.Path; import java.nio.file.Paths; public class ModuleRootPath { @Test public void getModuleRootPathTest(){ Path path = Paths.get("").toAbsolutePath(); System.out.println(path); } }获取类路径classpath
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; /** * 获取编译后的类路径位置, 相当于Spring框架中classpath, 对应Maven项目中的java和resource目录 */ public class ClassesPath { @Test public void getModuleRootPath2Test() { String path = getClass().getResource("/").getPath(); System.out.println(path); } }



