类关系结构
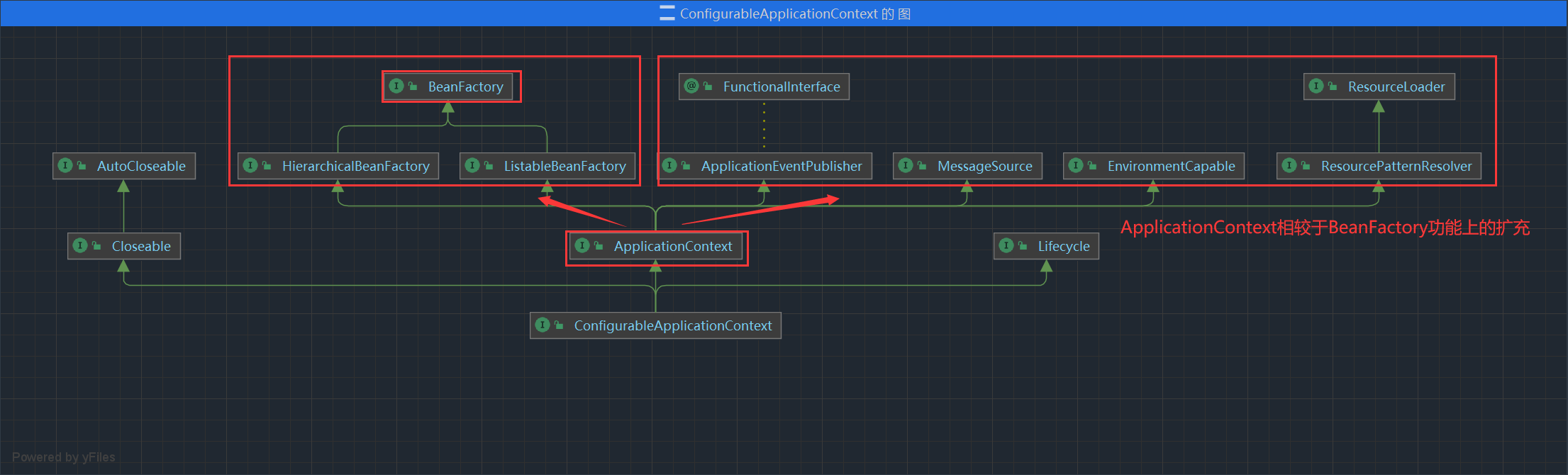
BeanFactory 功能介绍
BeanFactory 是核心容器,负责管理 Bean 对象
BeanFactory 接口的功能只有一个
getBean()方法BeanFactory 的实现类(
DefaultListableBeanFactory)包含:控制反转、基本的依赖注入、Bean 生命周期的各种功能,不能只考虑接口功能import lombok.SneakyThrows; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.Map; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringApplicationMain { @SneakyThrows public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SpringApplicationMain.class, args); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); // 通过反射方式来获取私有成员变量 Field singletonObjectsField = DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.class.getDeclaredField("singletonObjects"); singletonObjectsField.setAccessible(true); Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = (Map<String, Object>) singletonObjectsField.get(beanFactory); // 事先已经通过注解为Spring容器中注入两个以"component_"开头的组件, 这里过滤得到 singletonObjects.entrySet().stream() .filter(e -> e.getKey().startsWith("component_")) .forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getKey() + " = " + e.getValue())); } }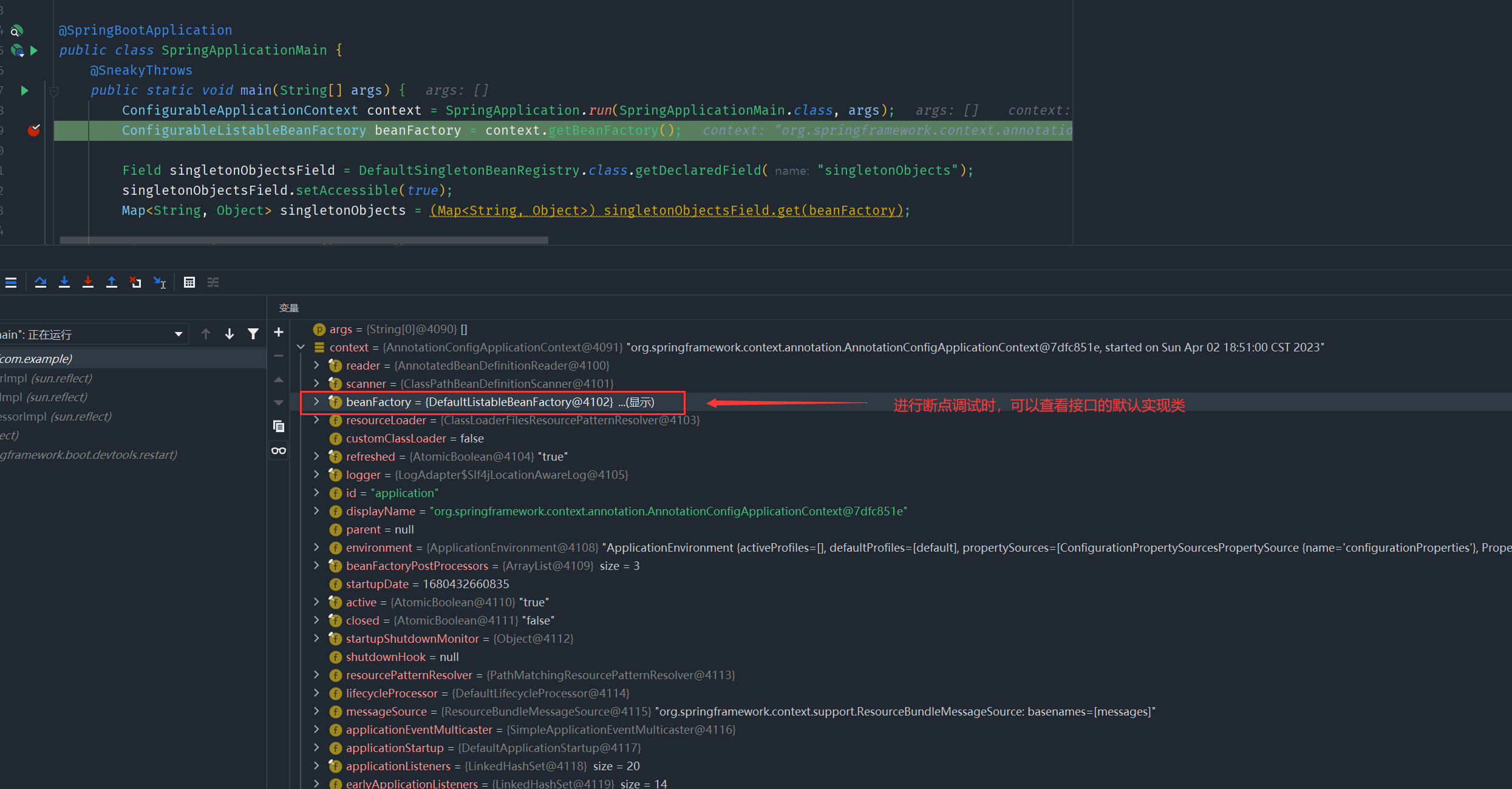
ApplicationContext 功能介绍
| 接口 | 功能 |
|---|---|
MessageSource |
国际化的能力 |
ResourcePatternResolve |
根据通配符去匹配文件资源(磁盘路径、类路径等) |
ApplicationEventPublisher |
发布事件对象(ApplicationEvent) |
EnvironmentCapable |
读取系统环境变量或配置文件中的信息,定义获取 Environment 方法 |
MessageSource 接口
使用方法
提供了 getMessage() 方法,以实现国际化的能力
需要准备各种不同语言的资源,例如
messages_en.properties和messages_zh.properties文件hi=Hello user=userhi=嗨 user=用户提供
resource_en.properties和resource_zh.properties文件username=username password=passwordusername=用户名 password=密码通过调用
getMessage()来获取资源import lombok.SneakyThrows; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.Map; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringApplicationMain { @SneakyThrows public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SpringApplicationMain.class, args); // 默认情况下, 文件必须以"messages.properties"命名 String hiZh = context.getMessage("hi", null, Locale.CHINA); String hiEn = context.getMessage("hi", null, Locale.ENGLISH); System.out.println(hiZh); System.out.println(hiEn); // 默认情况下会报错, 希望正常运行需要进行一些配置 String usernameZh = context.getMessage("username", null, Locale.CHINA); String passwordEn = context.getMessage("password", null, Locale.ENGLISH); System.out.println("usernameZh = " + usernameZh); System.out.println("passwordEn = " + passwordEn); }额外对Spring配置文件
application.properties进行修改spring.messages.basename=messages,resource
源码解析
找到自动配置类
MessageSourceAutoConfiguration@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) // 1. 自动配置类标配@ConditionalOnMissingBean注解 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = AbstractApplicationContext.MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE) // 2. @Conditional注解, 在ResourceBundleCondition注入之后进行注入, 指定前置依赖项 @Conditional(ResourceBundleCondition.class) // 3. @EnableConfigurationProperties搭配@ConfigurationProperties使用 @EnableConfigurationProperties public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration { private static final Resource[] NO_RESOURCES = {}; // 4. MessageSourceProperties配置类, 对应一些默认配置项 @Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.messages") public MessageSourceProperties messageSourceProperties() { return new MessageSourceProperties(); } @Bean public MessageSource messageSource(MessageSourceProperties properties) { ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource(); if (StringUtils.hasText(properties.getBasename())) { messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils .commaDelimitedListToStringArray(StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(properties.getBasename()))); } if (properties.getEncoding() != null) { messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(properties.getEncoding().name()); } messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(properties.isFallbackToSystemLocale()); Duration cacheDuration = properties.getCacheDuration(); if (cacheDuration != null) { messageSource.setCacheMillis(cacheDuration.toMillis()); } messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(properties.isAlwaysUseMessageFormat()); messageSource.setUseCodeAsDefaultMessage(properties.isUseCodeAsDefaultMessage()); return messageSource; } protected static class ResourceBundleCondition extends SpringBootCondition { private static ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<String, ConditionOutcome> cache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>(); @Override public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { String basename = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("spring.messages.basename", "messages"); ConditionOutcome outcome = cache.get(basename); if (outcome == null) { outcome = getMatchOutcomeForBasename(context, basename); cache.put(basename, outcome); } return outcome; } private ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcomeForBasename(ConditionContext context, String basename) { ConditionMessage.Builder message = ConditionMessage.forCondition("ResourceBundle"); for (String name : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(basename))) { for (Resource resource : getResources(context.getClassLoader(), name)) { if (resource.exists()) { return ConditionOutcome.match(message.found("bundle").items(resource)); } } } return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.didNotFind("bundle with basename " + basename).atAll()); } private Resource[] getResources(ClassLoader classLoader, String name) { String target = name.replace('.', '/'); try { return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(classLoader) .getResources("classpath*:" + target + ".properties"); } catch (Exception ex) { return NO_RESOURCES; } } } }查看配置文件类
MessageSourceProperties// 这里使用lombok注解对一些冗余代码进行修改 @Getter @Setter public class MessageSourceProperties { /** * Comma-separated list of basenames (essentially a fully-qualified classpath * location), each following the ResourceBundle convention with relaxed support for * slash based locations. If it doesn't contain a package qualifier (such as * "org.mypackage"), it will be resolved from the classpath root. */ private String basename = "messages"; /** * Message bundles encoding. */ private Charset encoding = StandardCharsets.UTF_8; /** * Loaded resource bundle files cache duration. When not set, bundles are cached * forever. If a duration suffix is not specified, seconds will be used. */ @DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.SECONDS) private Duration cacheDuration; /** * Whether to fall back to the system Locale if no files for a specific Locale have * been found. if this is turned off, the only fallback will be the default file (e.g. * "messages.properties" for basename "messages"). */ private boolean fallbackToSystemLocale = true; /** * Whether to always apply the MessageFormat rules, parsing even messages without * arguments. */ private boolean alwaysUseMessageFormat = false; /** * Whether to use the message code as the default message instead of throwing a * "NoSuchMessageException". Recommended during development only. */ private boolean useCodeAsDefaultMessage = false;
public boolean isFallbackToSystemLocale() {
return this.fallbackToSystemLocale;
}
public boolean isAlwaysUseMessageFormat() {
return this.alwaysUseMessageFormat;
}
public boolean isUseCodeAsDefaultMessage() {
return this.useCodeAsDefaultMessage;
}
}
```ApplicationEventPublisher 接口
使用方法
自定义一类事件
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; public class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent { // source代表事件源, 即谁发送的事件 public MyEvent(Object source) { super(source); } }自定义一个或多个事件监听器(任意一个Spring组件即可)
import com.example.event.MyEvent; import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; // 任意一个Spring组件都可以作为事件监听器 @Component public class MyEventListenerComponent { // 方法参数需要和监听的事件类型保持一致, 例如发送的事件类型是String.class, 那么方法参数中也应该是String.class @EventListener public void getStringEvent(String message){ System.out.println("String Event"); System.out.println(message); } @EventListener public void getMyEvent(MyEvent myEvent){ System.out.println("MyClass Event"); System.out.println(myEvent); } }使用 ApplicationContext 中的功能进行事件发布
import lombok.SneakyThrows; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringApplicationV5Main { @SneakyThrows public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SpringApplicationV5Main.class, args); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); context.publishEvent("Hello Event"); context.publishEvent(new MyEvent(context)); } }




