Interrupt方法详解
Interrupt打断阻塞态线程
打断阻塞态的线程会抛出异常,同时清空打断状态。该异常常用来作为唤醒手段
public class InterruptBlockedMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// 目前看来, 打断标志在执行异常处理前就被重新设置为false.
// 目前认为打断标志经历: false(初始值) -> true(主线程调用interrupt()方法) -> false(清空打断状态)
// todo: 打断标志是否会进行更改? 如果实际上没有更改那么如何检测到被打断呢? 可能是直接抛出溢出, 根本没有修改打断标志
System.out.println("threadA.isInterrupted() = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, "threadA");
threadA.start();
// 为了确保threadA启动, 调用sleep()方法进入阻塞状态
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
threadA.interrupt();
// 判断threadA是否被打断
System.out.println("threadA.isInterrupted() = " + threadA.isInterrupted());
}
}Interrupt打断运行态线程
打断标志可以认为是线程与线程之间的一个接口,主线程调用
interrupt()是希望其他线程能够被打断,但实际的实现逻辑取决于其他线程的代码逻辑(由程序员编写)。即interrupted打断标志并不能真正意义上的停止线程。
isInterrupted() 方法不会清空打断标志
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class InterruptRunningMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
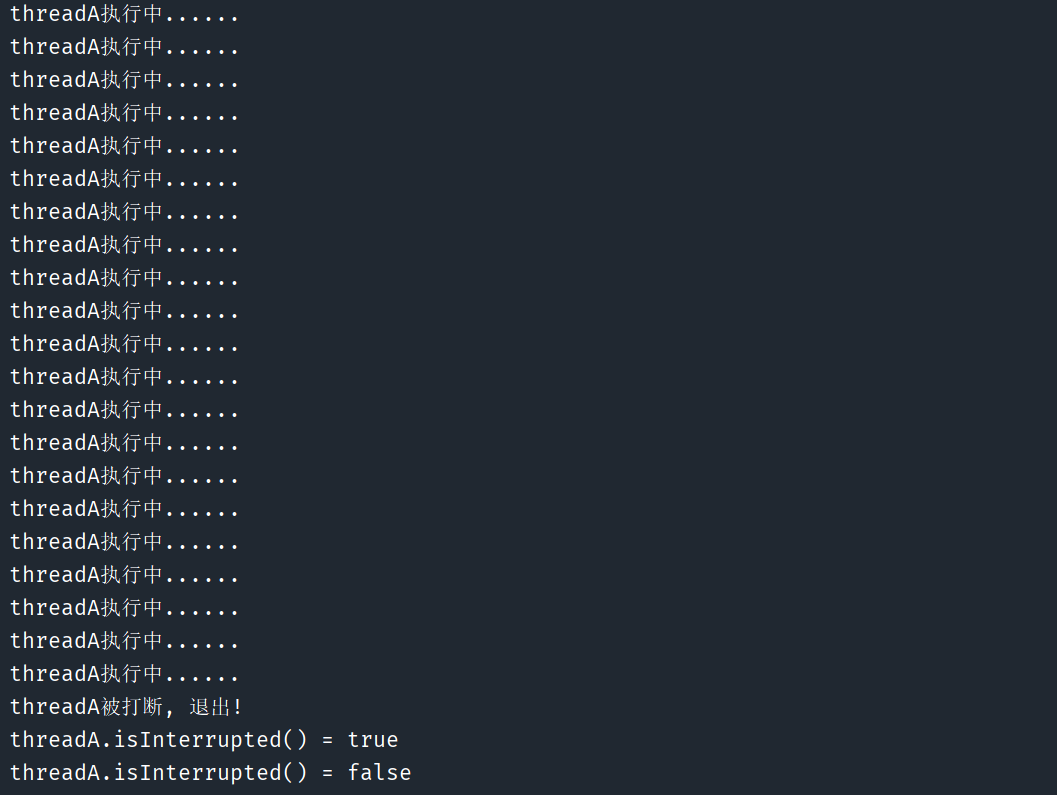
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
// 线程被打断, 执行退出逻辑
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "被打断, 退出!");
// interrupted() 不会清空打断标志, 所以这里输出true
System.out.println("threadA.isInterrupted() = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行中......");
}
}, "threadA");
threadA.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
threadA.interrupt();
System.out.println("threadA.isInterrupted() = " + threadA.isInterrupted());
}
}
interrupted() 方法清空打断标志
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class InterruptRunningMainWithCleanFlag {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
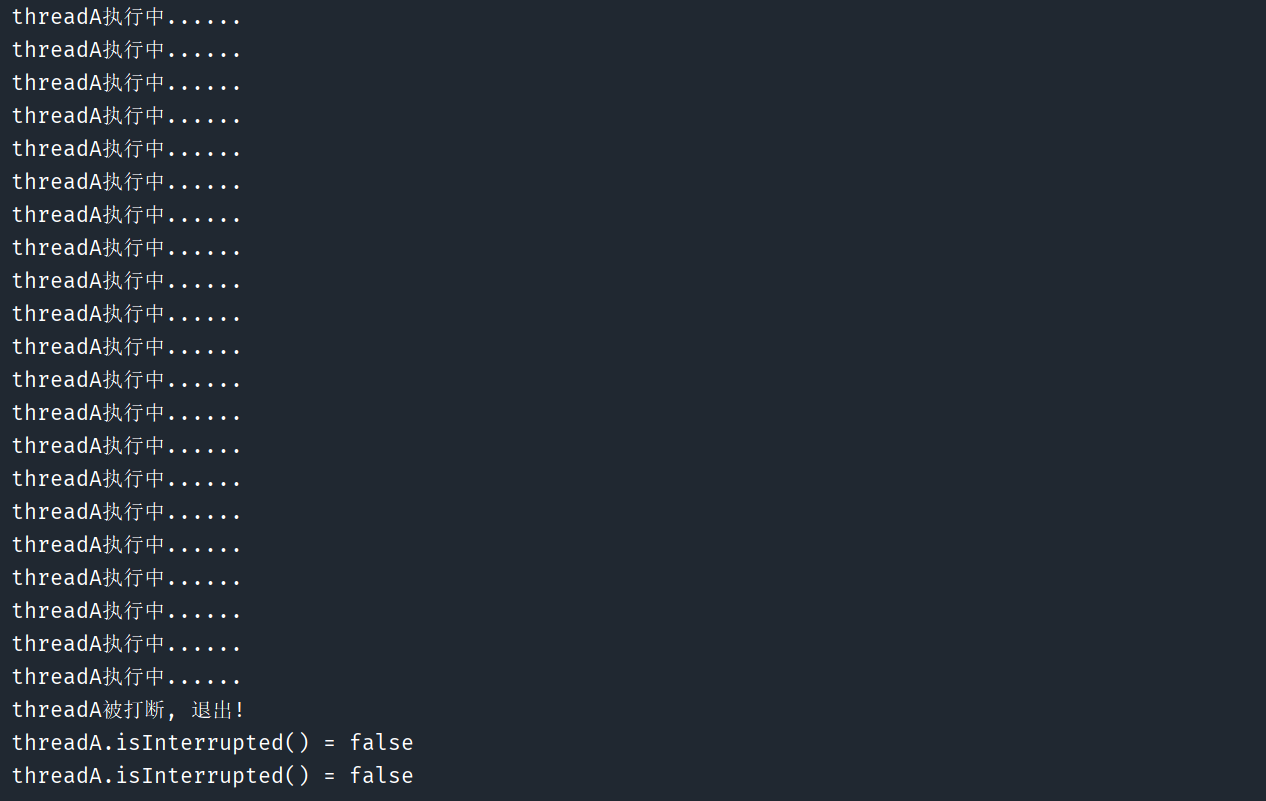
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
// 线程被打断, 执行退出逻辑
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "被打断, 退出!");
// interrupted() 会清空打断标志, 所以这里输出false
System.out.println("threadA.isInterrupted() = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "执行中......");
}
}, "threadA");
threadA.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
threadA.interrupt();
threadA.join();
// 这里线程结束后打断标志重置为默认值
System.out.println("threadA.isInterrupted() = " + threadA.isInterrupted());
}
}
两阶段终止模式
不合适的思路
使用
stop()方法强制杀死线程直接杀死占用锁的线程,会使得其无法释放锁,导致其他线程无法获取该锁
使用
System.exit()方法退出整个程序小题大做
使用interrupt实现优雅退出的两阶段终止模式
应用场景
例如监控程序,每隔一段时间执行一次,相比于上面的直接打断运行态线程的方式,两阶段终止模式由于使用了sleep(),所以对CPU的占用更小。监控进程每隔一段时间执行一次即可,不需要 while(true) 死循环重复不断地执行。
两阶段的含义
- 第一阶段:考虑线程被中断时处于运行态的情况
- 第二阶段:考虑线程被中断时处于阻塞态的情况
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TwoPhaseTermination {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
boolean exitFlag = false;
while (true) {
if (exitFlag || Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
// 如果被打断, 进行善后处理, 然后退出
System.out.println("执行善后处理工作, 优雅退出");
break;
}
// threadA的处理逻辑
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "监控中...");
// 如果没有被打断
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
exitFlag = true;
// 这里也可以不使用exitFlag变量来辅助判断, 再次执行interrupt()重新设置打断标志即可, 取消下面注释即可
// Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}, "threadA");
threadA.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
threadA.interrupt();
}
}
interrupt打断park线程
park()是LockSupport类中的一个方法,作用也是阻塞线程,但其原理是通过判断打断标志interrupted:
- 如果打断标志为false,那么会阻塞
- 如果打断标志为true,那么相当于没有效果
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class InterruptParkMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
// interrupted打断标志为false, pack生效, unpack time cost接近10s(主线程sleep的时间)
System.out.println("######################################################");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ".isInterrupted() = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("park");
LockSupport.park();
System.out.println("unpack time cost: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin));
// interrupted打断标志为true, pack失效, unpack time cost接近0
System.out.println("######################################################");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ".isInterrupted() = " + Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("park");
LockSupport.park();
System.out.println("unpack time cost: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin));
}, "threadA");
threadA.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
threadA.interrupt();
}
}



